Recombinant human CD30 protein
| 【No.】IRP029A | 【Protein name】 Recombinant human CD30 protein |
| 【Gene Sequence Number/Expression Region】P28908/19-379 | 【Label position】C-terminal Human-Fc Tag |
| 【Restriction sites】Enterokinase | 【Packing specification】100μg/tube |
CD30 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. It belongs to a type I transmembrane protein. It is overexpressed in Hodgkin’s lymphoma and gradual large cell tumor lymphoma, and it is underexpressed in T cells and B cells activated in non-case conditions. Surface, while normal cells do not express [1] . Early studies have shown that CD30 is involved in cell activation and differentiation, NF-kB and other signal transduction, and T cell immune activation. Current studies have confirmed that CD30 is closely related to cell proliferation and death, and its intracellular part can be related to TNFR-related factor families. The interaction between these members can not only mediate cell apoptosis through the JNK and p38 pathways, but also mediate cell activation through the NF-kB pathway [2,3] . After CD30 is activated, its extracellular part is quickly degraded by proteases to form soluble sCD30. CD3O is commonly expressed on the surface of HL and ALCL cells and can be used as a potential target for antibody targeted therapy. This product is a CD30-FC recombinant protein (FC tag can be removed by enterokinase), which can be used for monoclonal antibody screening or antibody function verification.
Product name: Recombinant human CD30 protein
Species: Human origin
Gene sequence number: P28908
Tags: Human-Fc Tag
Tag site: C terminal
Restriction site: enterokinase
Expression area: extracellular segment 19-379
Host cell:CHO
Purity: >90%
Purification method: Protein A column
Preservation system: PBS+20% glycerol
Storage conditions: -80℃
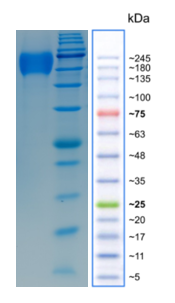

The molecular weight of the protein is 40.4kDa. The protein migration rate under reduction conditions is 60-100kpa.
Reference materials:
1.T cell receptor-dependent cell death of T cell hybridomas mediated by the CD30 cytoplasmic domain in association with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors
2. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 5 and TRAF2 are involved in CD30-mediated NFkappaB activation
3. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)-1, TRAF-2, and TRAF-3 interact in vivo with the CD30 cytoplasmic domain; TRAF-2 mediates CD30-induced nuclear factor kappa B activation

