Recombinant human PDL1 protein (PDL1-FC)
| 【No.】IRP139A | 【Protein name】 Recombinant human PDL1 protein |
| 【Gene Sequence Number/Expression Region】NP_054862.1/(19-238AA) | 【Label position】C-terminal Human-Fc Tag |
| 【Restriction sites】None | 【Packing specification】100μg/tube |
Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a member of the B7 super family, once named B7-H1 and CD274 . It is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that can be widely expressed and activated The surface of T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. At the same time, it is also expressed in some immune shielding parts of the body such as placenta, eyes, epithelium, muscle, liver, vascular endothelial cells and other tissues. Studies have shown that PD-L1 is overexpressed in most cancer tissues, including NSCLC, melanoma, breast cancer, glioma, and lymphoma. And high expression of PD-L1 can inhibit RAS and PI3K / AKT and inhibit T cell proliferation or induce cell signaling pathways like CTL apoptosis; may be reduced by mTOR, AKT, S6 and ERK2 phosphorylation and regulation of PTEN promoting Induces the production of Treg , and then inhibits the activity of effector T cells. This product is a PD-L1 (19-238AA)-FC recombinant protein, which can be used for monoclonal antibody screening or antibody function verification.
Product name: Recombinant human PD-L1 protein
Species: Human origin
Gene sequence number: NP_054862.1
Tags: Human-Fc Tag
Tag site: C terminal
Restriction site: none
Expression area: extracellular segment ( 19-238A A)
Host cell: CHO-S
Purity:> 90%
Purification method: Protein A column
Preservation system: PBS+20% glycerol
Storage conditions: -80℃
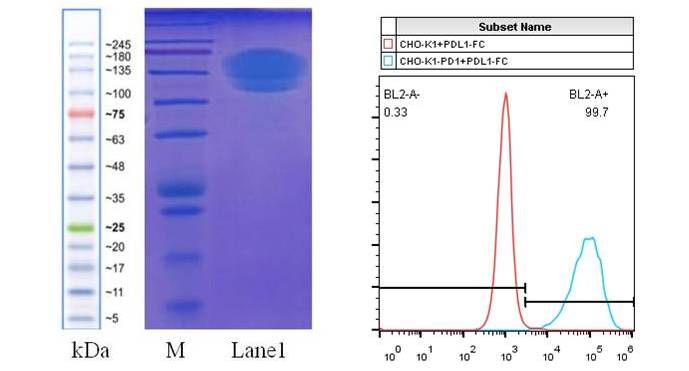
Illustration: Lane M on the left is the protein MW marker, Lane 1 is the 10ug PD-L1-Fc protein;
The right image shows the FACS detection of the binding of PD-L1-FC protein to CHO-K1 overexpressing PD-1
Reference materials:
1. The PDL1-PD1 Axis Converts Human TH1 Cells into Regulatory T Cells
2. PDL1 Is Required for Peripheral Transplantation Tolerance and Protection from Chronic Allograft Rejection
3. Prognostic and predictive value of PDL1 expression in breast cancer
4. A Link between PDL1 and T Regulatory Cells in Fetomaternal Tolerance
5. PDL1 Regulation by p53 via miR-34

